What Are Wisdom Teeth?
“Wisdom teeth” are a type of molar. Molars are the large chewing teeth found furthest in the back of the mouth. Most people have 1st, 2nd and 3rd molars. A person’s third molars are their wisdom teeth. (See the picture on the left).
When Do Wisdom Teeth Come In?
For most people, the eruption process usually takes place between the ages 18 to 24 years. In many instances there is not enough room for the wisdom teeth to erupt fully.
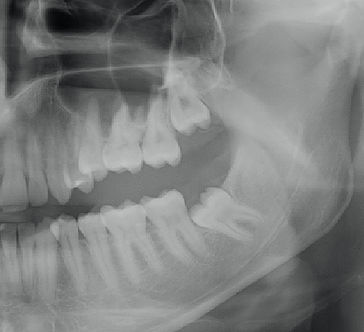
What Are Impacted Wisdom Teeth?
In dental terminology, an “impacted” tooth refers to one that has failed to fully erupt into its expected position.
This failure to erupt properly usually occurs due to lack of space in that person’s jaw. As you can see in the x-ray above, the path of eruption is obstructed by the 2nd molar tooth because of the angulation of the wisdom tooth.
Are There Different Type’s Of Impacted Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth may be either mesial, distal, horizontal or vertically impacted. These terms are used to refer to the general angulation (positioning) of the tooth.
- The term “Mesial” (also mesio-angular) means that the crown of the tooth is angled forward, toward the second molar. This is the most common type of wisdom tooth impaction
- A Distal (also disto-angular) impaction has an angulation that is generally directed towards the oppsoite side of the mesial.
- Horizontal (also traverse) impactions have an alignment where the tooth is lying on its side.
- Vertical impactions have a relatively normal orientation. Almost parallel to the other molars.
Why Should I Have My Wisdom Teeth Removed?
Wisdom teeth are the last teeth to erupt within the mouth. When they align properly and are fully erupted and clear of all surrounding gum tissue, wisdom teeth do not have to be removed. Unfortunately, this does not commonly happen. The extraction of wisdom teeth is necessary when they are prevented from properly erupting within the mouth.
These poorly positioned impacted teeth can cause many problems. When they are partially erupted, the opening around the tooth allows bacteria to grow between the tooth and the gum and will eventually cause an infection. The pressure from the erupting wisdom tooth may encourage crowding and orthodontic relapse. The conatct pont betweent the wisdom tooth and the second molar is usually difficult to floss and on the long term can lead to cries on the 2nd molar. The most serious problem occurs when tumors or cysts form around the impacted wisdom tooth, resulting in the destruction of the jawbone and possibly other healthy teeth. Removal of the offending impacted tooth or teeth usually resolves these problems. Early removal is recommended to avoid such future problems and to decrease the surgical risk involved with the procedure.
Oral Examination
With an oral examination and x-rays of the mouth, positiong of the wisdom teeth can be evaluated and an assessment made about their extraction. Studies have shown that early removal result in a superior outcome for the patient. Patients are generally first evaluated in the mid- teenage years by their dentist, orthodontist or by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Removal
The removal of wisdom teeth could be performed under local anaesthesia, or general anaesthesia. These options as well as the surgical risks (i.e. sensory nerve damage, sinus complications, etc) will be discussed at a consultation appointment with you before the procedure is performed. The options of anesthetic will be discussed and a detailed financial quote will be given.
